Resistance temperature detectors (RTD) measure temperature by raising electrical resistance as temperatures increase. RTD sensors are made of platinum or other pure metals and display a small linear positive change for every degree of temperature difference.
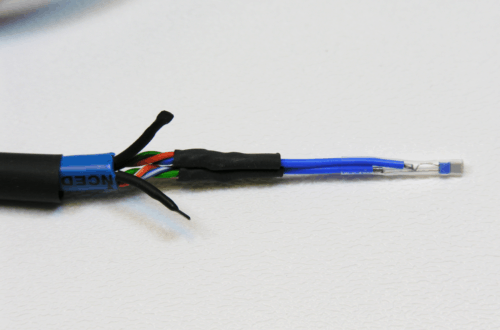 What Are RTD Probes?
What Are RTD Probes?
RTD probes are a type of temperature sensor that measures temperatures in labs and industrial applications. A protective sheath wraps around the metal resistance element, which is placed into the measuring area. An electrical current travels through the RTD probe’s resistor to generate a resistance value.
As the temperature of the RTD probe’s metal increases, the resistance to electrical flow also increases. This change in resistance is predictable and determines the temperature reading. RTDs provide optimal repeatability, stability, and accuracy for temperatures up to 400 °C, though they can withstand temperatures up to 1000 °C.
Common Types of RTD Probes
Depending on the intended use, RTD probes come in the following types.
Thin Film
Thin film RTD probes feature a thin metal layer on ceramic substrates. To provide sufficient resistance, the film is etched into a certain electrical circuit pattern. These flat RTD sensors are reliable, rugged, shock and vibration resistant, and available in a range of sizes, shapes, and tolerances.
Wire Wound
These RTD probes are wrapped in wire, outside the probe’s glass or ceramic housing. Unlike other types of RTD sensors, these are submersible in liquids. They are more expensive than thin film sensors because of their advanced nature, but ceramic wire round RTDs offer superior accuracy in extreme temperatures.
Coiled
Coiled RTD probes consist of thin wound wires inside a glass or ceramic housing containing nonconductive powder. Due to its ability to expand and contract with temperature changes, the sensor minimizes errors resulting from mechanical strain.
Pt1000
The pt1000 RTD is a platinum sensor with a resistance factor measuring 1000 Ω, and it is most commonly implemented in two wire applications. These sensors need less electrical current, making them suitable for configurations using reduced power.
Two Wire
Two wire RTD sensors use a simple circuit design consisting of a lead wire that connects to each end of the probe. The device calculates resistance through measurements of the connectors and wires, which can lead to higher-than-actual temperature measurements, but calibration can easily correct this issue.
Three Wire
The three wire RTD sensor is popular in industrial applications. These probes have two wires connected to the monitoring device and one end of the probe’s sensor, with a third wire connecting to the element.
Four Wire
These RTD sensors feature the most complex designs, making them costly and time-consuming to install. In return, they provide the most precise and accurate measurements. Two lead wires supply DC current, while two other leads measure voltage drop.
Common Components of RTD Probes
A typical probe consists of an element, a lead wire, a sheath, and a connection. Further components must then be selected based on the probe’s intended application. These components include wiring arrangements, wire materials, connection type, and configuration.
Wiring Arrangement
The element of an RTD probe must connect to control or monitoring equipment. With the exception of two wire RTD probes, all wiring arrangements enable the control or monitoring equipment to eliminate any other undesired resistances and produce accurate temperature readings.
Wire Materials
The temperature of the installation environment will dictate which wire insulation materials to select. Three popular options include PVC, PFA, and fiberglass.
Termination or Connection
RTD probes may use a quick disconnect, connection head, extension wire, or terminal block for termination. Other termination types can be customized for your particular RTD probe.
Configuration
Following component selection, configuration is the final consideration. It depends on whether the probe will measure liquid, gas, or surface temperatures, as well as other environmental factors.
Benefits and Applications of RTD Probes
These are some of the benefits of measuring temperature with RTD probes:
- Cost-effectiveness
- Sensitivity
- Accuracy
- Linearity
- Stability
- Wide temperature range
RTD probes have a wide array of applications in these and other industries:
- Automotive
- Pharmaceutical
- Chemical
- Medical
- Food processing
- Aerospace
High-Quality Custom RTD Probes from Digital Instruments
At Digital Instruments, we offer reliable custom RTD probes and electronic solutions for our customers. We operate from a comprehensive facility with state-of-the-art technology, and our team of experienced technicians and designers can work with you from concept to completion.
If you would like to learn more about our RTD probes or other products, feel free to request a quote or contact us with any questions.
